
Lavender Fragrance oil
Lavender oils and hydrosols contain more than 100 compounds with the two major constituents being linalool and linalyl acetate. Formed with terpenoids, lavender is a middle note that brings calming, floral and herbaceous aroma. With a scent that lasts longer than top notes, lavender is widely used in perfumery because of its versatility.
Hi, my name is Alexandra and I am a French undergraduate student in the second year of a bachelor degree in chemistry. I am specialized in analysis and would like to work in green chemistry.
I am doing my internship at the University of Ottawa and work on the chemical composition of hydrosols. I hope to learn more about the functioning of the GC-MS but also how it is used to analyse samples.
I had the opportunity to work on lavender and more precisely on the components of the different forms of lavender products : hydrosol, essential oil and fragrance oil.
This allowed me to compare the results of a microwave distillation with a hydro distillation. I was also charged of the analysis and comparison of the essential oil, complex mixture of volatile chemicals derived from the roots, leaves, flowers, and fruits of plants, with the fragrance oil which is a blended synthetic aroma compounds or natural essential oils that are diluted with a carrier.
Being a widely used plant, the documentation about lavender is necessary and I am more than grateful to be a part of it.

Analytical technique
Gaz Chromatography Mass Spectroscopy is an analytical method used to identify the volatile organic molecules that have a boiling point under 300 Celsius degrees. Helium, that is not detected by the device, is constantly in circulation and plays the role of a carrier gaz. The injection of 1 µL of sample is done to the septum level which vaporizes the sample and leads it into a spiral column. After that, the GC oven ramp heats the column making the components elute according to their boiling points and interactions with the column. Then, the mass spectrometer ionizes and fragments the molecules leading to their specific mass spectra equivalent to a fingerprint. Finally, the comparison of the obtained spectra with the data base allows us to identify the components of the sample. Several parameters such as the inlet temperature, the oven temperature and the ramp can be modified depending on the analyzed sample.
The GC-MS offers high sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility in different analyses. It can detect molecules even at trace levels in complex matrices, making it a valuable tool for research and industry.

Lavender essential oil
We may not really realize it, but essential oils play a key role in our daily lives. Without the molecules that make them up, the world would have neither aroma nor smell. Indeed, the fragrance of flowers, the Ventolin for asthmatics, or even the smell of cosmetic products are all directly linked to the presence of essential oils.
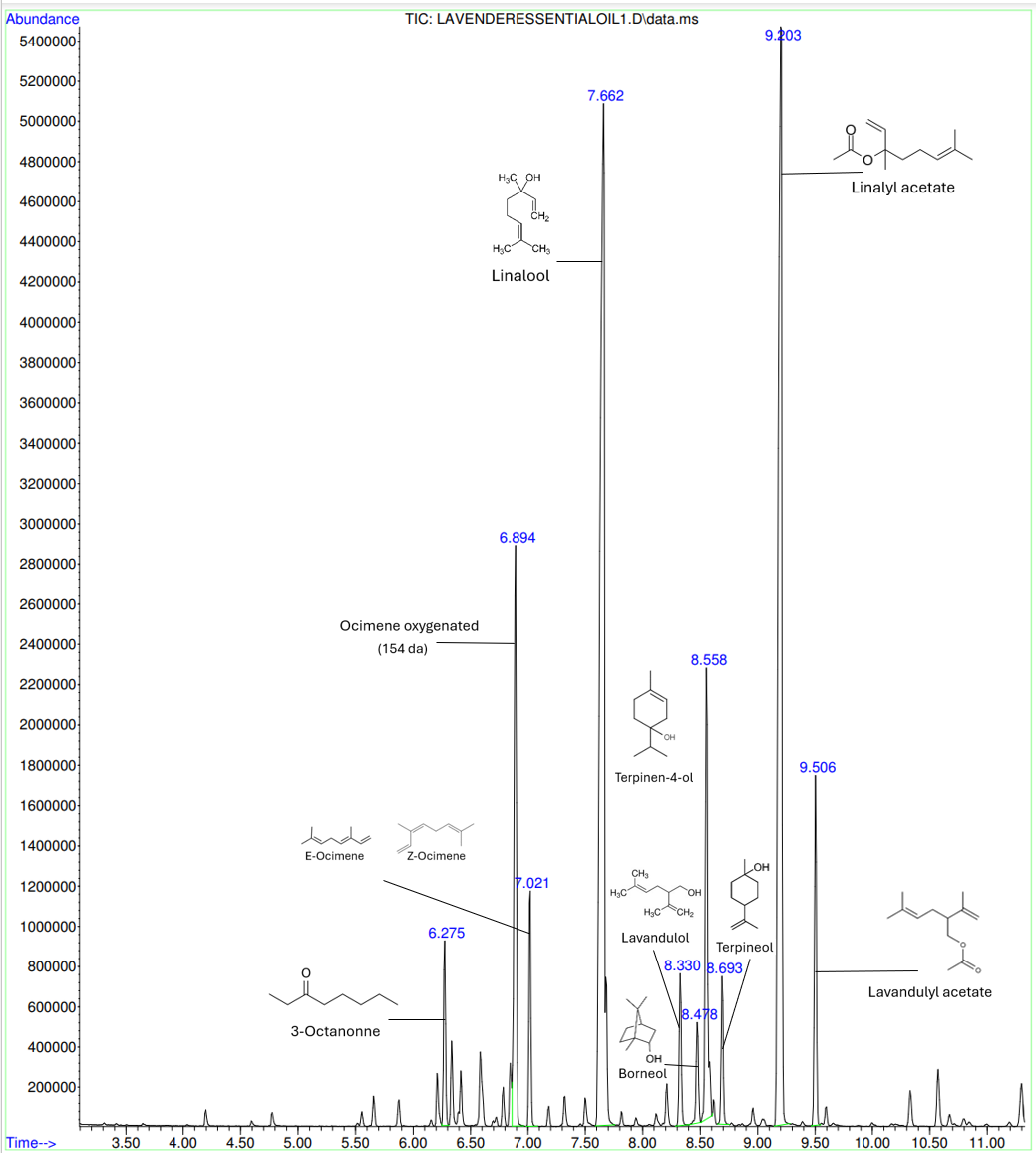
I had the opportunity to study a commercial lavender essential oil in order to identify its components but also their role in the formula. To do this analysis, I have diluted my essential oil to have a 0.5mg/mL concentration for the sample. Indeed, because the density of the lavender essential oil is of 0.885g/mL, I need to put 0.565 µL of product in 1mL. To have a simplest pick-up value and because the maximum concentration for the GC-MS is 1 mg/mL instead of 0.5mg/mL, I have decided to mix 1µL of essential oil into 2mL of ethyl acetate which is my solvent. For the analysis, I have modified the parameters to have a better resolution and result. Indeed, the GC-MS starts at 40 Celsius degrees for 2 minutes and increases of 15 Celsius degrees per min until 150°C. The inlet is at 150°C and the analysis takes 12 minutes.

The analysis was done three times, and a comparison of the results was made. The average is an estimation of the true value corresponding to the entire population when we only have a sample of all the possible measurements. The variance is the measure of the dispersion of values in the sample, the standard deviation is a measure of the dispersion of the values of the statistical sample and the relative standard deviation, called coefficient of variation when express in percentage, is the measure of the relative dispersion. The more those parameters are small, the more the measurement is accurate, and the values are closed one to each other.
Indeed, in the case of this study, we can see that the coefficient variation of the retention time is very small, not exceeding 0,05%, which means that the chemicals are always detected at the same retention time. The temperature of the GC-MS increasing of 15 Celsius degrees per minute leads to the detection of each component of the sample according to their boiling point. Thus, the same chemical has a fixed retention time that is specific to him.
However, the percentage area fluctuates a little more but remaining weak. This parameter corresponds to the percentage of each component in the 1 µL of injected sample. Indeed, the variation of this value is due to the fact that the different chemicals of the sample are not perfectly mixed.

The main active ingredients in this lavender essential oil are monoterpenes: linalool, linalyl acetate, lavandulol, borneol, terpineol and lavandulyl acetate, which is the acetate ester of lavandulol. They are used to create a pleasant smell as well as ocimene and 3-octanone. Indeed, linalool is a terpene alcohol that is commonly found in natural essential oils and contribute to the overall scent of a fragrance with a floral and spicy scent. Linalyl acetate and lavandulol are natural compounds found in lavender and are at the origin of a sweet scent of lavender. All those chemicals contribute to the aromatic profile of the essential oil but also to its therapeutic properties such as skin care and inhalation function. For example, the terpinene-4-ol is a monoterpene renowned for its potent antimicrobial properties.
This essential oil has the characteristic and very recognizable smell of lavender that we all know. Bringing freshness to perfumes, it has a note of bergamot, a little floral but also a more herbaceous and camphorous side.
Moreover, I made a comparison of my GC-MS results with the results of the essential oil from another website and I have observed that almost all compounds are common to both product and have more or less the same proportions.
Lavender fragrance oil
This analysis aims to study the mixture of natural and synthetic molecules that is used to recreate the famous lavender smells. Also, the objective is to compare the obtained results with the molecules present in the headspace and detected by SPME. Finally, this will allow me to compare if the same chemical components are present in the essential oil and in the fragrance oil of lavender. It will feature the non-natural chemicals of the fragrance oil that were added by the industry. I expect to find linalool in my sample as well as compounds such as additives or preservatives.
The analysis of 1 µL of a sample containing 1µL of lavender fragrance oil and 2mL of ethyl acetate was conducting by GC-MS. A lot of components are present in this fragrance oil, but we will focus on the 12 main compounds.
Lavandula angustifolia, also called English lavender, has an extremely high essential oil content and fragrance. Used for centuries to produce perfumes, candles and bug spray, it has notes of musk, rosemary, bergamot and geranium. This type of lavender originates from the mountains of the Mediterranean and is commonly used on the culinary domain thanks to its earthy and minty leaves.
The French lavender, Lavandula dentata, has a more subtle fragrance than English lavender and is native from Spain. Its smell is less light and sweet because of a higher content of camphor that provides a woody scent making it a perfect cleaning product. Blooming nonstop from early summer to late fall, French lavender is a precious decorative element for gardeners thanks to its famous purple flowers.
These two lavender fragrance oils have distinct and more complex scents. Indeed, even if their heart note is similar to a lavender-like scent, these fragrances differ in their overall aromatic profile. From my point of view, I consider English lavender to have a more herbaceous and woody smell while the French lavender has a spicy and camphorous aroma.

First, the French lavender and English lavender have some chemicals in common: α-pinene, D-limonene, eucalyptol, linalool, camphor, citronellol, linalyl acetate and benzyl benzoate. α-pinene is a terpene found in oils that has anti-inflammatory properties. Used in candles for its pine-like aroma, it offers some properties to repel insects. The D-limonene is a cyclic monoterpene used as solvent in cleaning products and perfumeries. Its fresh and citrusy scent makes it a perfect candle ingredient that is appreciated for its energizing qualities. Eucalyptol, also known as 1.8-cineole, is a monoterpenoid that has a distinctive refreshing and camphor-like aroma. Found in several oils such as citronella and rose oils, citronellol is a natural monoterpenoid and valuable ingredient in the creation of aromatic and functional candles. Finally, benzyl benzoate is an organic compound used as an insect repellent that has a sweet and balsamic aroma. It helps in dissolving and evenly dispersing the other components of the fragrance. Thus, the chemicals that are present in both fragrance oils mainly contributes to the overall scent of the formula.

French lavender fragrance oil
The French lavender contains numerous other products in more or less large quantities. Indeed, ethyl maltol, that represent almost 6.5% of the total oil, blends well with the other compounds by providing a sweeter smell. Found naturally in many flowers, benzyl acetate is the ester of acetic acid and benzyl alcohol and makes up the top scent of jasmine. In candles, this chemical enhances the overall fragrance profile with its floral and fruity aroma. Chrysanthone, also called isophorone, is a terpenoid derived from chrysanthemum oil the offers a refreshing and relaxing scent of flower. α-cetone, presented as α-isomethyl ionone, has a pleasant aroma and is stable over time. On the other hand, methyl(Z)-dihydrojasmonate is a synthetic fragrance compound that has a scent reminding the one of jasmine. In this way, this fragrance oil is composed of natural and synthetic compounds used for their smell and stability in candle formulas and which were added by the candle industry.

English lavender fragrance oil
For its part, English lavender turned out to be less complex, bringing together only 16 chemical compounds instead of 23. We can talk about coumarin, an organic chemical compound found in many plants and that has been used for centuries in the perfumery industry through its comforting scent. The patchouli alcohol or patchoulol is a sesquiterpene leading to the possession of a higher boiling point and therefore a greater retention time. Moreover, α-terpinyl acetate is a natural organic compound found in essential oils that belongs to the terpene chemical class and is commonly used in perfumery and aromatherapy due to its pleasant aroma and potential therapeutic properties.
Musks are fragrant natural compounds produced by several animals and a few plant species that are used in perfumes. Indeed, chemists have synthesize a series of artificial musks, including galaxolide (a polycyclic musk present in the French lavender fragrance oil), muscone, and musk ketone. The latter is an aromatic musk that dates to 1888, when a German chemist made it serendipitously while he was trying to produce the explosive TNT. In the perfume and candle industries, musk ketone is called a fixative because it stabilizes the volatility and improves the tenacity of perfume aromas.

SPME
A SPME analysis of the fragrances’ head space was conducted with the following set up. The GC-MS parameter used for this method were the same as before but with an inlet temperature 200°C. However, based on the chromatograms obtained and the absence of chemical compounds with high boiling points, the use of this method does not require raising the temperature that high. Indeed, only the most volatile compounds are present in the headspace and correspond to small molecules.

As the chromatograms shows, the molecules visible aren’t very numerous and six of them are common to both fragrances, there is linalool, eucalyptol, d-limonene and linalyl acetate for example. The English lavender headspace also contains 2-octanone, citronellol, α-terpinyl acetate and benzyl benzoate while in the French lavender we can see cymene as well as thujone. It is a plant-derived volatile monoterpene ketone found in various plants used for flavoring food and drinks. In vitro studies have shown that thujone has both genotoxic and carcinogenic properties, alongside antimutagenic and immune-modulatory effects. Additionally, research suggests that thujone may have antidiabetic and antimicrobial activities.

Conclusion
To conclude, thanks to those analysis, I was able to compare the components of the lavender hydrosol, essential oil, and fragrance oil. It allowed me to define was compounds are common to all of them and which one were not. In the end, linalool is the only chemicals that I have found into all my samples. Lavender hydrosols, essential oils, and fragrance oils differ significantly in their chemical composition due to the distinct extraction processes used and the specific nature of the compounds they capture.
The results of the GC-MS analysis of the fragrance oils has shown a great consistency with the theorical properties and components of those plants described before. Actually, French lavender is more bitter because of a higher content of camphor of 6.81% against 2.98% for the English lavender. Furthermore, English lavender is widely known for its notes of musk that are represented by the synthetical musk ketone with an area percentage of almost 1%. The candle industry has used natural lavender compounds but also organic chemicals from other plants to recreate this famous scent. A few synthetic compounds were added to the formula to complete the fragrance’s aroma but also to act as solvents and mix evenly the ingredients.
These differences are linked to the nature of the production method. Steam distillation, used for essential oils and hydrosols, separates volatile components based on their boiling points. Essential oils capture the full range of volatiles, whereas hydrosols retain more water-soluble fractions. On the other hand, synthesis or blending, used for fragrance oils, focuses on replicating the scent profile using isolated aromatic chemicals.
Documenting these compositional differences is crucial for their therapeutic use since the effectiveness of hydrosols and essential oils depends on their specific chemical constituents. For safety and efficacy, understanding the chemical profiles aids in assessing potential allergenic or toxic effects, ensuring safe usage, especially in formulations applied directly to the skin.
